5. Interlude - Process API
Go over fork(), exec(), and wait()
The fork() System CallThe fork() system call is used to create a new processOn success, the PID of the child process is returned in the parent, and 0 is returned in the child..
12345678910111213141516171819202122#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>intmain(int argc, char *argv[]){ printf("hello world (pid:%d)\n", (int) getpid()); int rc = fork(); if (rc < 0) { // fork failed; exit ...
4. The Abstraction - The Process
A process is a running program.Running many processes at a time is done by virtualizing the CPU (like time-sharing).
ProcessTo understand what constitutes a process, we have to understand its machine state: what a program can read or update when it is running.
Machine State: Key ComponentsMemory (Address Space): The code (instructions) and the data the program uses are stored in memory. The “address space” of a process is all the memory addresses it can use.Registers: Registers are very small st ...
OSTEP intro
What happens when a program runs?The processor fetches an instruction from memory, decodes it, and executes it. Then the processor moves on to the next instruction until the program completes.
The operating system is a software responsible for making it easy to run programs, allowing programs to share memory, enabling programs to interact with devices, and other fun stuff.(This is often done through virtualization so the OS is sometimes referred to as a virtual machine)
OS is sometimes known as ...
08 Tree Indexes
Table IndexesThere are a number of different data structures one can use inside of a database system. For table indexes, which may involve queries with range scans, a hash table may not be the best option since it’s inherently unordered.
A table index is a replica of a subset of a table’s columns that is organized and/or sorted for efficient access using a subset of those attributes. Although more indexes makes looking up queries faster, indexes also use storage and require maintenance. Plu ...
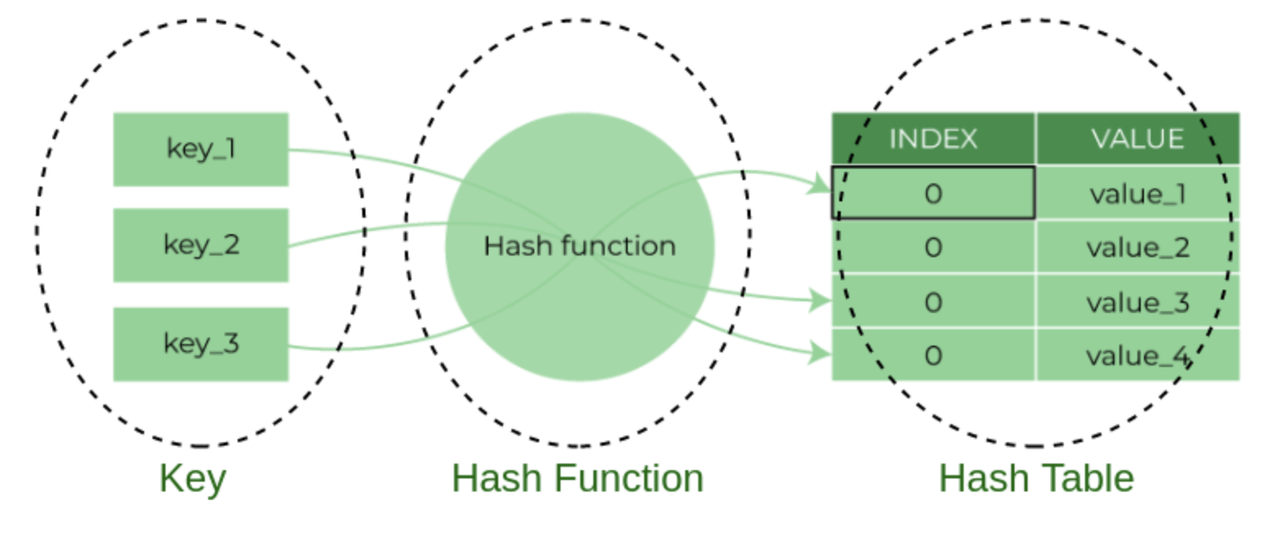
07 Hash Tables
Data StructuresA DBMS uses various data structures for many different parts of the system internals.Some examples include:
Internal Meta-Data: Information about the database and the system state
Core Data Storage: The actual data (tuples) we want to store
Temporary Data Structures: Temporary data structures while processing a query to speed up execution (eg, hash tables for join)
Table Indices: Auxiliary data structure to find specific tuples
There are two main design decisions to consider w ...
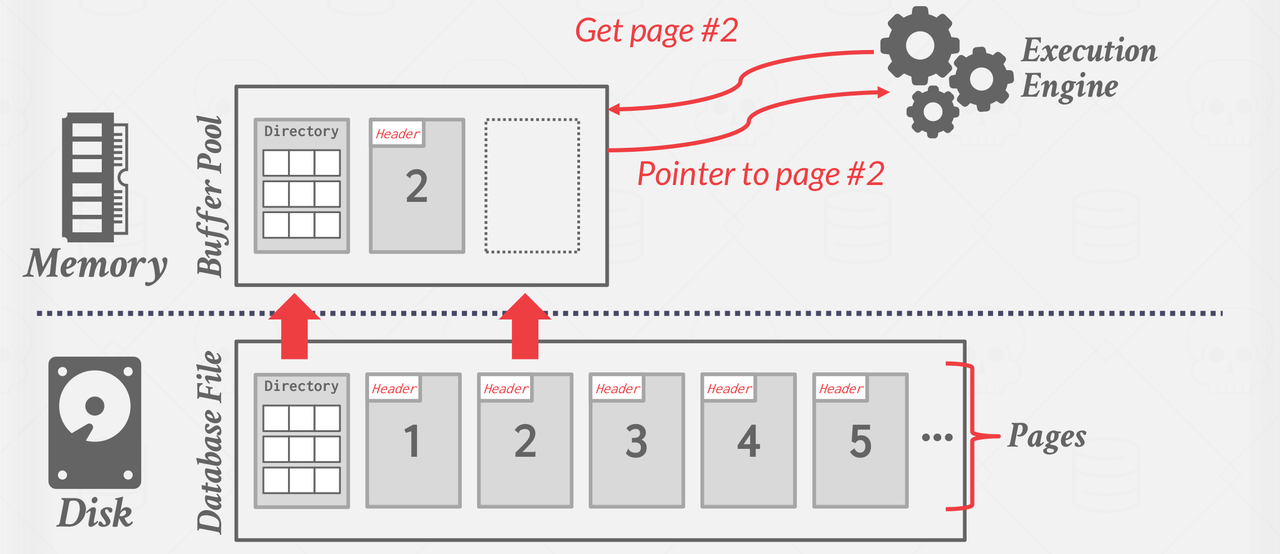
06 Buffer Pools
IntroductionThe DBMS is responsible for managing its memory and moving data back and forth from the disk. Since, for the most part, data cannot be directly operated in the disk, any database must be able to efficiently move data represented as files from disk into memory so that it can be used.
Another way to think of this problem is in terms of spatial and temporal control:Spatial Control aims to keep pages that are used together often as physically close together as possible on disk.Tempor ...
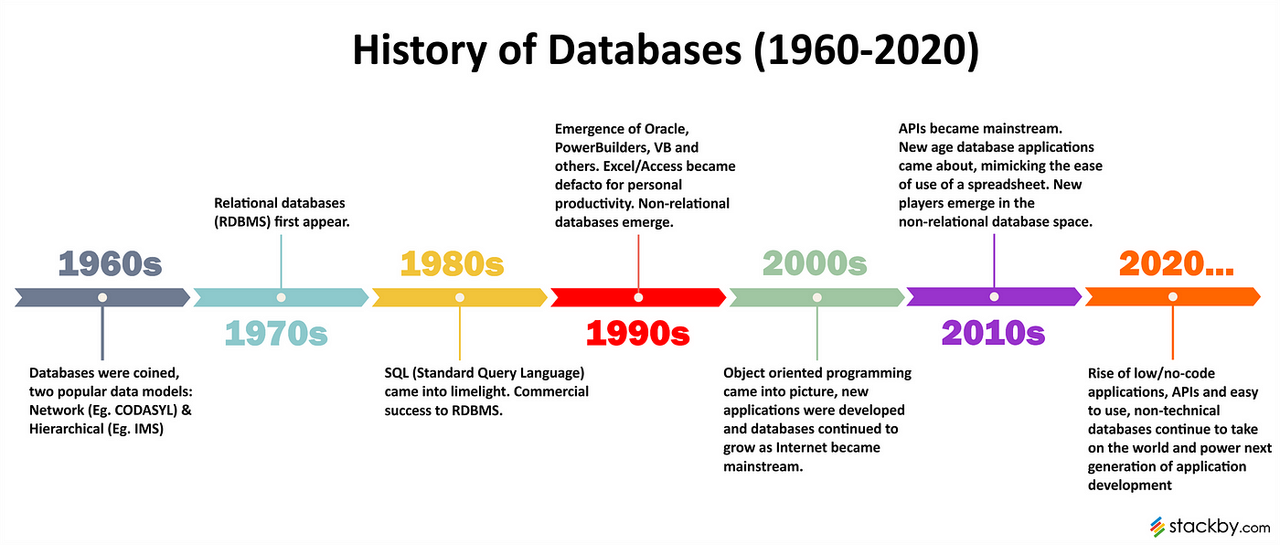
Tracing the Evolution and Modern Advances of Databases Models
Basic introduction to a database?A database is an organized collection of data, generally stored and accessed electronically from a computer system. Databases make it possible to manage, store, and retrieve information efficiently. The core purpose of a database is to enable users to access and manipulate data in a structured way. A high-performing database is crucial to organizations that have big amounts of data. Also, databases are essential for efficient scaling, data integrity, data secur ...
A Guide on SSH
Disclaimer: This post does not go in depth for each of the Operating Systems since there are far too many. However, I will use Ubuntu Linux as an example for this guide.
What is SSH?SSH, or Secure Shell, is a network protocol used to securely access and manage a computer over an unsecured network. It provides a secure channel over an otherwise insecure network by using a client-server architecture, allowing users to log into another computer over a network, execute commands in a remote mac ...
Future Study Plans
This post includes a list of topics I plan to study in the future.
My Study Priority Queue:
Basic Overview on the History of Databases and the Different Types of Databases
Relational Database (Buffer Pools, Hash Tables, Tree Indexes, Index Concurrency Control, etc…)
C++
OS basics
Machine Learning basics
SQL (may be postponed)
Network basics (maybe not)
Random topics I find interesting (nginx, ssh, compiler, ninja, linux (maybe ubuntu maybe other distros), gnome, cli, gcc, bash, etc…)
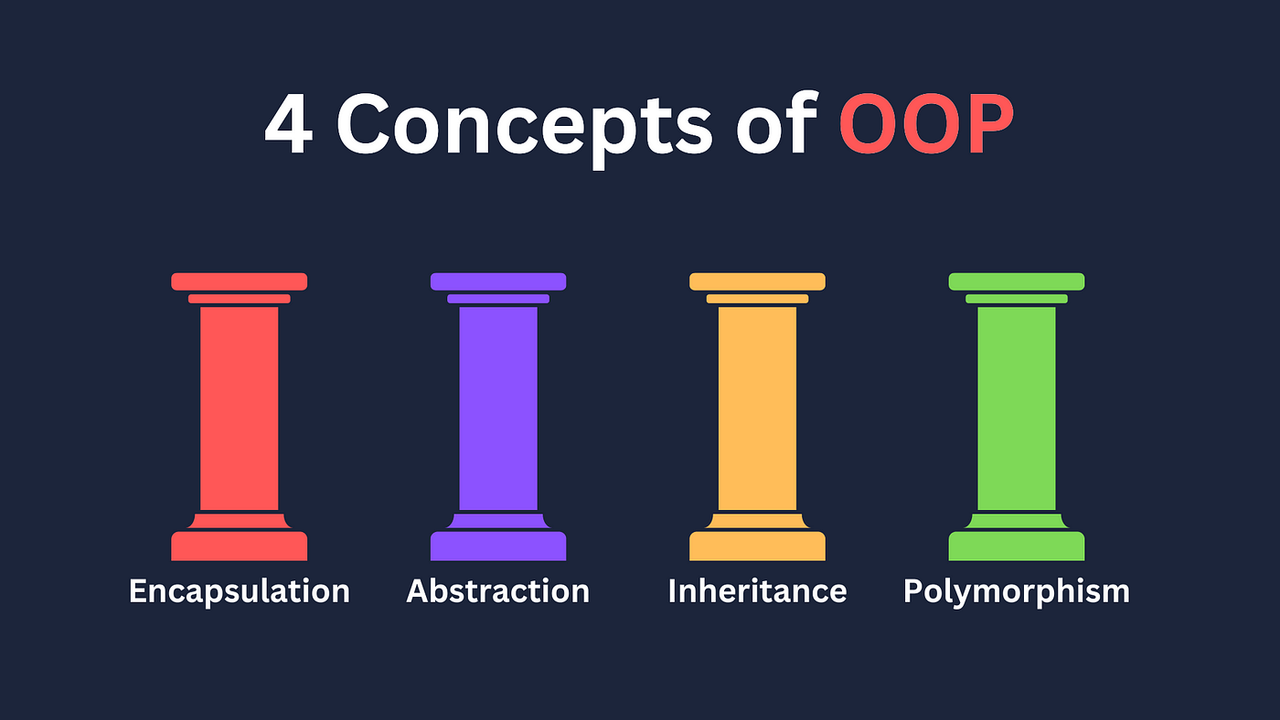
Object-oriented Programming
This note was taken after studying Concepts of Programming Languages by Robert W. Sebesta, 10th edition.
Object-oriented ProgrammingA language that is object-oriented must provide support for 3 key language features:
Abstact data types (classes)
Inheritance
Dynamic binding of method calls to methods
InheritanceProblems with abtract data types:
Some features and capabilities of the existing types are not always adequate for use. The old type requires at least some minor modifications.
Give ...